Install Gainsight PX SDK for Android
This article explains how developers can use Gainsight PX’s Android SDK to set it up in their application.
Overview
The Gainsight PX Android SDK is a powerful tool that can measure your application’s statistics and provide you with powerful insights about your app. This article explains the various facets of including Gainsight PX Android SDK in your Android app.
Gainsight PX provides you with an Android archive (.aar extension) file. You can use this file to set up a project in any mobile application development platform. (This article uses the Android Studio application.)
This article consists of the following sections:
Installation
Android-SDK is available as a dependency through Maven.
- Add the repository into build.gradle file for App level (root level repositories not buildscript)
repositories {
...
maven {
url "https://github.com/Gainsight/px-android/raw/main/"
}
}
- Add the dependency to build.gradle file (App level)
dependencies {
...
implementation 'com.gainsight.px:mobile-sdk:1.10.1'
}
Note: The version number gets regularly updated.
For more information on how to install Android-SDK, refer to the GitHub article.
- Click here to view the alternate Installation method.
-
Add Android Archive File to Project
This section explains how you can use the Gainsight PX .aar file in your project.
- Download and extract the Gainsight PX .aar file.
- Launch the Android Studio application.
- Navigate to File > New > New Module.

- Select the Import .JAR/ .AAR Package and click Next.
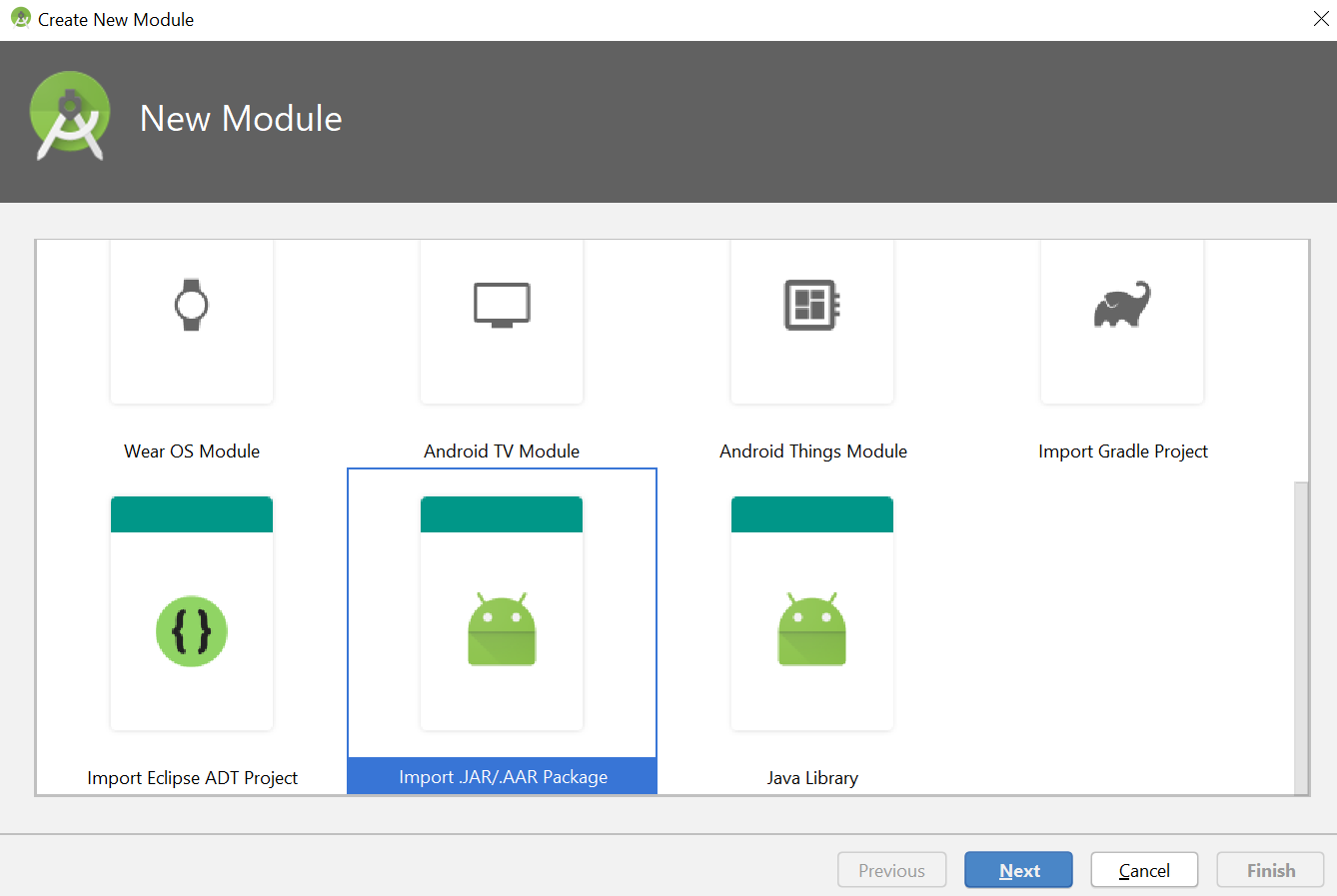
- Click the folder icon, navigate to the location of your .aar file, and select it.
- Click Finish
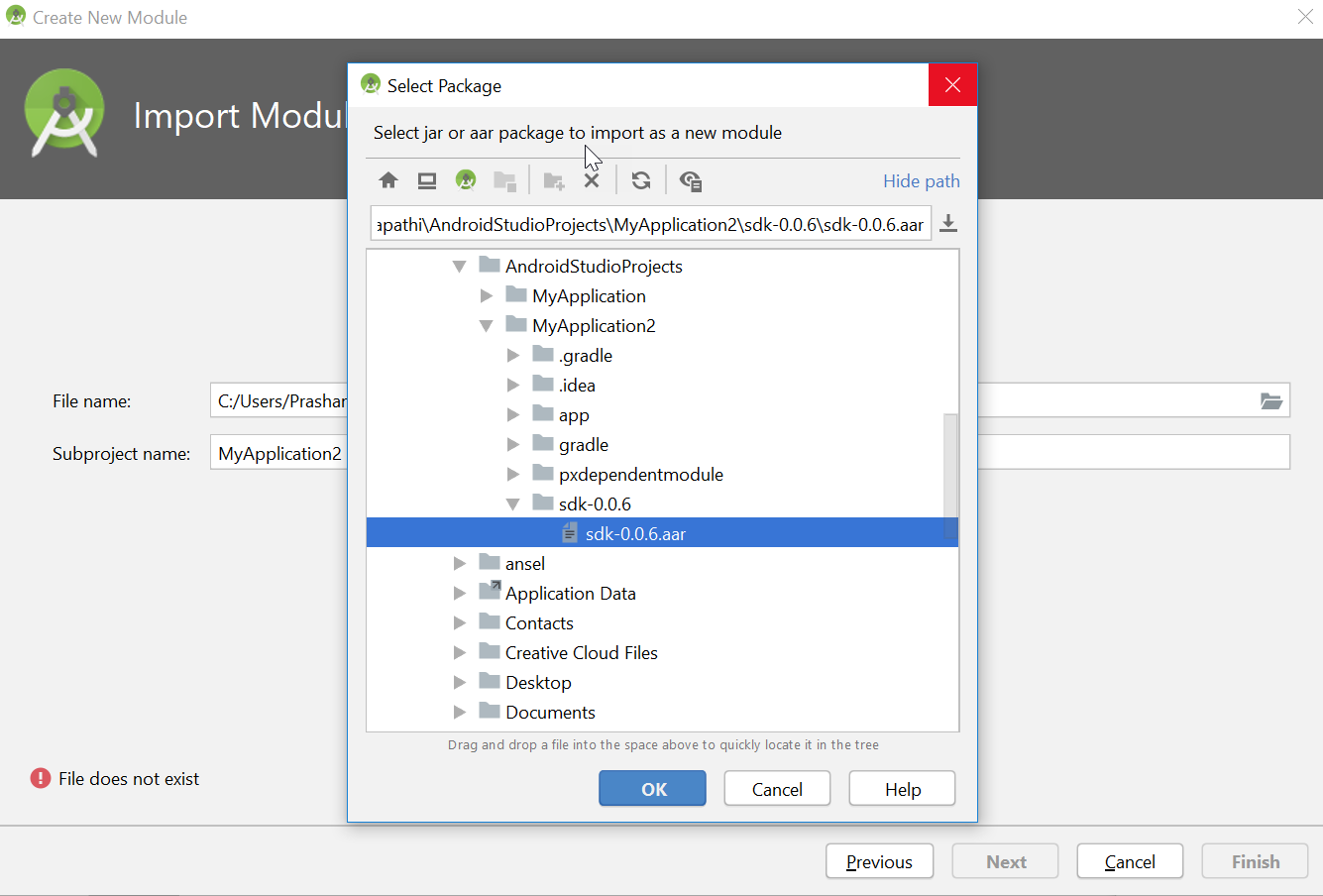
- Add the newly created module as a dependency module of other modules:
- Right-click your Gainsight PX module and select Open Module Settings.
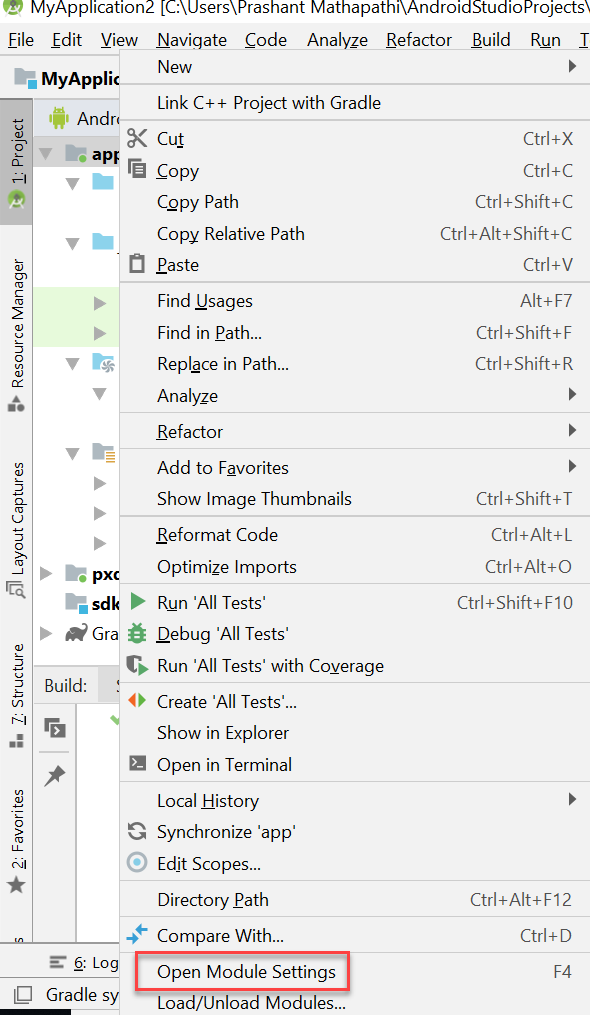
- Click Dependencies in the left pane.
- Click + and select Module dependency.
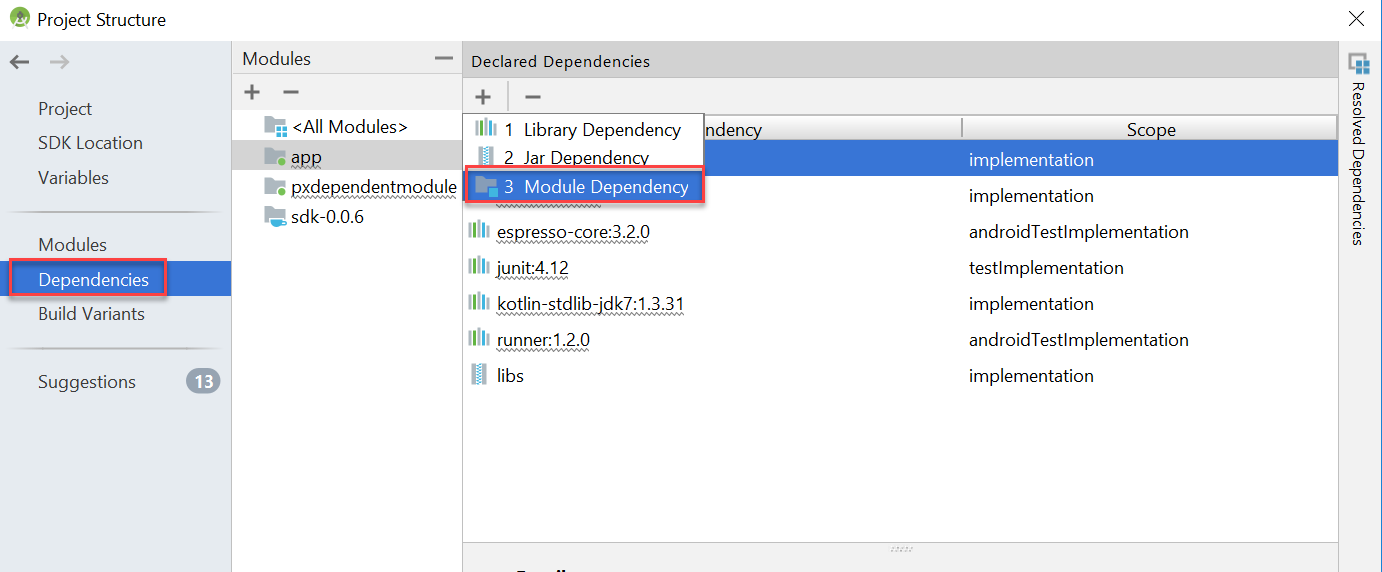
- Select the checkbox for the required modules.
- Click OK.
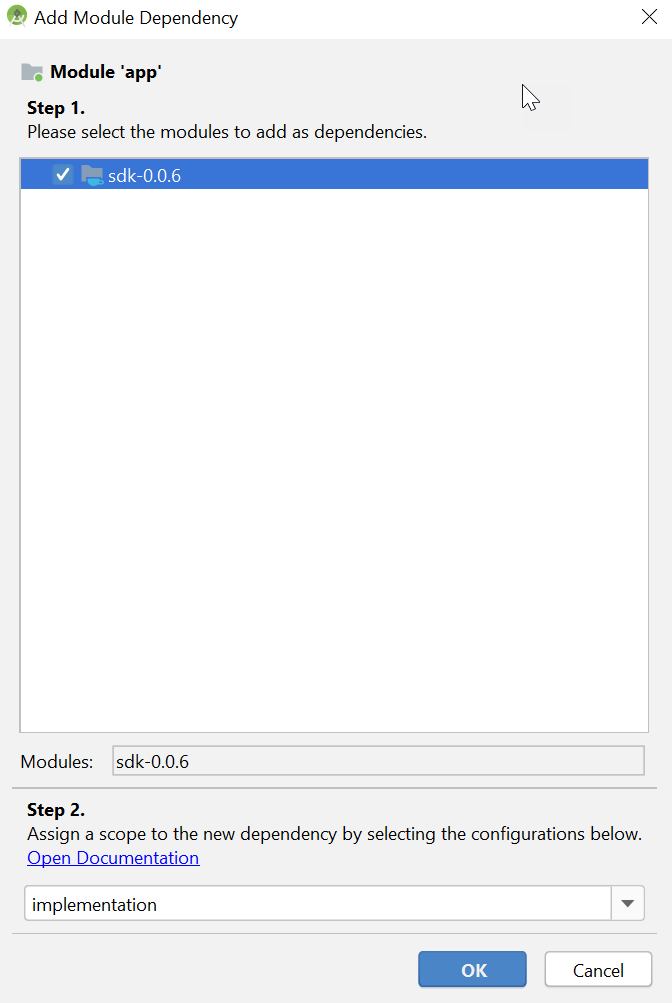
- Right-click your Gainsight PX module and select Open Module Settings.
Integrate Gainsight PX Editor
Gainsight PX Mobile Editor helps you manage PX engagements and Product Mapper from your mobile application.
The In-app Editor allows you to:
- Preview engagements in the mobile app
- View the Product Tree
- Create, edit and delete Module/Features
- Add Tap Rules for Module/Features
To use the in-app editor, copy the Scheme to integrate your mobile application with the your platforms that Gainsight supports.
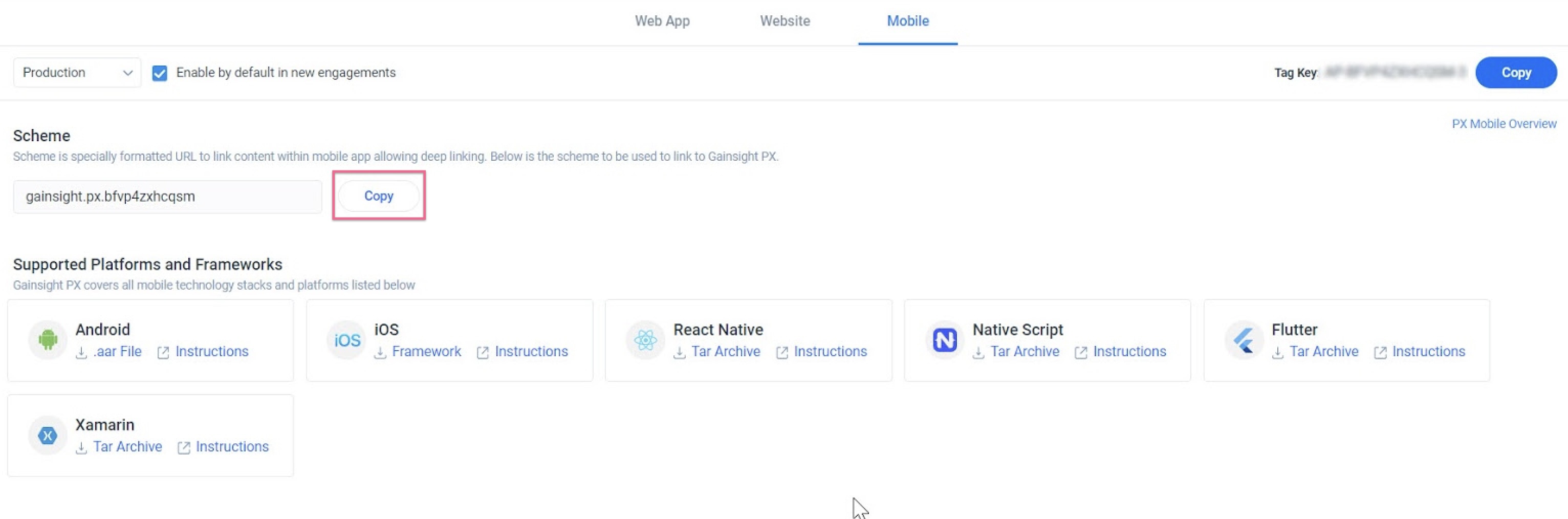
You can activate the editor using deep linking and forwarding the link to the SDK. While forwarding the information, you as a developer have the ability to implement your own logic and permissions before launching the editor.
Prerequisite: Deep linking must be enabled to access the Gainsight PX Editor. For more information on how to create deep links, refer to the Android documentation article.
To integrate Gainsight PX with the Android platform:
- Add the following to your app AndroidManifest.xml file, in the main activity part:
<intent-filter>
<data android:scheme="{SCHEME}" />
<action android:name="android.intent.action.VIEW" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.BROWSABLE" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" />
</intent-filter>
Note: Setting host attribute is not required.
- After initializing the GainsightPX instance, call the following on the code for the same activity:
if ((null != intent) && (null != intent.getScheme())) {
GainsightPX.with().enterEditingMode(intent);
}
Note: You can use the same code on onNewIntent method as well:
if ((null != intent) && (null != intent.getScheme())) {
GainsightPX.with().enterEditingMode(intent);
}
Using Gainsight PX
This section explains how to get started with Gainsight PX mobile app development. You can customize the default settings as required. For more information, refer to the Gainsight PX Configuration section of this article.
Initialize
IMPORTANT: The following settings are the default configurations that are suitable for clients that are on the US data centers. For clients that are from EU or US2 data centers need to modify the default configurations mentioned in the Gainsight PX Configurations section as per the requirement.
To use the custom setting:
- Create a subclass of the Android Application class.
- Declare the subclass in the Android.Manifest file.
- Override the onCreate method to start an instance of GainsightPX.Builder, by using the following code.
GainsightPX.Builder builder = new GainsightPX.Builder(Context context, String YOUR_PRODUCT_ID);
- Configure the Builder with the required custom configurations.
- Call the Builder.build function to create a new instance of Gainsight PX, by using the following code.
GainsightPX instance = builder.build();
-
Setup Gainsight PX as a singleton instance, by using the following code.
GainsightPX.setSingletonInstance(instance);
IMPORTANT:
- You can call the above function if hardreset is not applied to it and you can reset the function.
- You can call the GainsightPX.with(), to start collecting data from your application, after setting the singleton instance.
Create Events
This section explains how to create events that can track data from your mobile application. Events are actions associated with your app and allow you to track various actions performed by users on your app. Currently, the Gainsight PX SDK supports four types of events.
App Events
App events track general operations performed on your application. App events do not require any configurations. The Gainsight SDK auto collects App events from your application. However, if you disable the App events collection, these events are not collected. The app events collected are as follows:
| Event Name | Description |
|---|---|
| APP_OPENED | Tracks every instance of customers launching your application. |
| APP_INSTALLED | Tracks every instance of customers installing your application. |
| APP_UPDATED | Tracks every instance of customers updating your application. |
Gainsight PX is also looking to launch two additional app events in the future; APP_BACKGROUNDED and APP_CRASHED. The former tracks every instance of your application running in the background and the latter tracks every instance of an app crash. However, these events are not auto-enabled, and have to be configured.
Screen Events
Screen events track various screens of your application, traversed by a user. By default, Gainsight PX tracks the screens of your application visited by users (if the user moves from the first screen to the second screen and then returns to the first screen, it is tracked automatically). However, in some situations, you need to explicitly register screen views. To help you in such situations, Gainsight PX has the following functions with PUBLIC access specifier:
GainsightPX.with().screen(@NonNull String screenName);
You can also create a screen event with additional properties (for example, parameters created for starting the page), as a map, by using the following code.
GainsightPX.with().screen(@NonNull String screenName, @Nullable final Map properties);
You can also create a screen event with fully loaded details like screen class, information from the intent that created the activity and so on. To accomplish this, use the following code.
GainsightPX.with().screen(@NonNull final ScreenEventData eventData);
Screen name is a mandatory argument to use any of the above functions.
Identify Events
These events are used to identify a user uniquely. Gainsight PX SDK provides you with three functions to identify users.
GainsightPX.with().identify(@NonNull String userId);
GainsightPX.with().identify(@NonNull User user);
GainsightPX.with().identify(@NonNull User user, final @Nullable Account account);
User ID is a mandatory argument to use any of the above functions. You can also use the User and Account objects to uniquely identify users. While creating either the User or the Account object, you must provide an ID. You can add more attributes to user information. There are setter methods for common attributes. However, you can add custom attributes using the following code:
user.putCustomAttributes(Map customAttributes); account.putCustomAttributes(Map customAttributes);
Custom Events
Custom Events are used to track specific events on your app. Currently, every button click is also tracked as a custom event. However, in future releases, button clicks will be tracked automatically. The functions of custom events are:
GainsightPX.with().custom(@NonNull String event); GainsightPX.with().custom(final @NonNull String event, final @Nullable Map properties);
Event Name is a mandatory argument. You can also add event properties to track further details of the event that occurred.
General Methods
This section describes the general methods (functions) of Gainsight PX SDK. There are three general methods:
| Method Name | Method | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Flush | GainsightPX.with().flush(); | This method sends all events on the queue to the server, by ignoring the scheduled auto flush. Generally, you need not use this method but there could be situations in which you may need to flush out events. |
| Reset | GainsightPX.with().reset(); | This method resets all user events. This method is generally used only when a user logs out of your application so that all future events can be grouped as part of the next login. |
|
ShutDown |
GainsightPX.with().shutdown() |
|
|
Enable |
GainsightPX.with().enableEngagements(boolean enable) boolean enabled = GainsightPX.with().enabled(); |
These methods help you to enable or disable event tracking on your app. When you use the disable method, no event is sent to the server. You can use the disable method on data sensitive areas of your app. |
Global Context
A global context can be set on the variables. You can set a global context with key-value pairs and send it with the payload. Global context can be set with Date, String, Double, and Boolean data types. Global Context data is stored at the memory level and not disk-level. The key-value pairs are sent with the Payloads. If an application is terminated, all the key-value pairs are erased.
The following code snippet can be used to set the global context data fields:
globalContextData = new GlobalContextData(); globalContextData.putString(key, stringValue); globalContextData.putNumber(key, longValue); globalContextData.putNumber(key, intValue); globalContextData.putNumber(key, doubleValue); globalContextData.putBoolean(key, booleanValue); globalContextData.putDate(key, dateObject); globalContextData.putDate(key, <#[String object with ISO8601 format]#>); globalContextData.putDate(key, <#[long for unix time in millisec]#>);
The following code snippet can be used to set the global context data fields:
GainsightPX.with().setGlobalContext(globalContextData);
The following code snippet can be used to check if the key is available:
if ((GainsightPX.with().getGlobalContext() != null) && (GainsightPX.with().getGlobalContext().hasKey("key"))) {}
The following code snippet can be used to remove the key from the global context:
GainsightPX.with().getGlobalContext().removeKey("key"{, "key2"...});
EngagementCallBack
Gainsight PX provides the Engagement Callback feature for mobile engagements that you create for mobile applications. This feature helps in receiving a callback for all button actions and URL clicks that the end-user performs on an engagement. Once you receive the callback, you can decide your next action like helping the user to navigate to a new screen, or perform an API call and so on.
Prerequisite
Ensure that you have installed/configured the Gainsight PX Mobile SDK v1.5.1 or above.
To use the Engagement Callback feature for Android devices, you need to implement the EngagementCallback interface.
Example:
public class GlobalEngagementCallback implements GainsightPX.EngagementCallback {
private static GainsightPX.EngagementCallback instance;
private final Context context;
private GlobalEngagementCallback(Context context) {
this.context = context;
}
public static GainsightPX.EngagementCallback instance(Context context) {
if (null == instance) {
synchronized (GlobalEngagementCallback.class) {
if (null == instance) {
instance = new GlobalEngagementCallback(context.getApplicationContext());
}
}
}
return instance;
}
@Override
public boolean onCallback(EngagementMetaData engagementMetaData) {
// Here you can do your functionality based on the callback.
return true;
}
}
While you initialize the SDK with the below function:
GainsightPX.Builder builder = new GainsightPX.Builder(Context context, String YOUR_PRODUCT_ID);
You can add the EngagementCallback functionality as follows:
builder.engagementCallback(GlobalEngagementCallback.instance(this))
EngagementMetaData Properties
The following table describes the properties in the arguments received from the EngagementCallBack event listener :
|
Property |
Type |
Description |
|
actionText |
string |
The text of the linked element. |
|
actionType/ |
string |
Refers to the element that invoked the Engagement Callback. |
|
engagementName |
string |
Name of the engagement for which the callback is received |
|
scope |
object |
Mobile screen scope where the engagement is shown. |
|
engagementId |
string |
ID of the engagement for which the callback is received . |
* actionData - reserved property for future usage; currently functions similar to actionText
* params - reserved property for future usage to send any custom parameters.
Error Handling
All exceptions occurred when creating events are passed into error callback GlobalExceptionHandler.
public class GlobalExceptionHandler implements GainsightPX.ExceptionHandler { private static GainsightPX.ExceptionHandler instance;
private Context context; private GlobalExceptionHandler(Context context) {
this.context = context;
} public static GainsightPX.ExceptionHandler instance(Context context) {
if (null == instance) {
synchronized (GlobalExceptionHandler.class) {
if (null == instance) {
instance = new GlobalExceptionHandler(context.getApplicationContext());
}
}
}
return instance;
} @Override
public void onExceptionOccurred(String methodName, ValueMap params, String exceptionMessage) {
String text = "Exception occurred in: " + methodName + ", With the message: " + exceptionMessage;
GainsightPX.with().logger(Constants.GAINSIGHT_TAG).debug(text);
}
}
The properties of onExceptionOccurred are as follows:
- The first parameter (methodName) informs about the invoked function name.
- The second parameter (params) gives the event properties that were sent to create an event.
- The error parameter (exceptionMessage) informs about the exception that occurred.
IMPORTANT:
You can add Exception Handler to any of the following methods:
- Builder
- Screen
- Identify
- Custom
Example:
GainsightPX.with().identify(@NonNull String userId, GlobalExceptionHandler.instance(context));
Gainsight PX Configurations
This section describes methods, whose configurations can be modified by you during the initialization stage.
| Method Call | Default | Description | Override by Server? |
|---|---|---|---|
| pxHost(PXHost host) | PXHost.US |
Setting the data center that Gainsight PX instance will send the events to. |
No |
| flushQueueSize (int size) | 20 | The number of events that are considered to form a batch to be sent to the server. Once this limit is reached, PX sends the events to the server even if it's still not the time for that (by the timer) | Yes |
| flushInterval (long value, TimeUnit unit) | 30 sec | The time interval during which the client checks if there are any new events to send to the server | Yes |
| collectDeviceId (boolean collect) | true | Whether or not to collect the device id from the device | No |
| tag (String tag) | {PRODUCT_ID} | Custom string to be used as part of the log string | No |
| logLevel (LogLevel logLevel) | NONE | Which log level should be logged to CatLog. By default, none will be logged | No |
| crypto (Crypto crypto) | None | Enables to add encryption for the data that is stored locally | No |
| trackApplicationLifecycleEvents (boolean shouldTrack) | true | Should the client auto track app related events (APP_OPENED, APP_INSTALLED and APP_UPDATED) | No (Server can drop the event based on remote configuration) |
| shouldTrackTapEvents | false |
Should the client auto-track tap events Note: Enabling this helps you track only the single tap gestures. |
Yes |
| recordScreenViews (boolean shouldRecord) | true | Whether or not the client should auto track | No (Server can drop the event based on remote configuration) |
| proxy (String proxyHost) | null | There's an option to send the network requests via proxy (mainly for security checks) | Yes |
| connectionTimeout (int value, TimeUnit unit) | 15 sec | Network connection timeout for getting any response from the server | Yes |
| readTimeout (int value, TimeUnit unit) | 20 sec | Network connection timeout for fully completing the network request | Yes |
| trackApplicationCrash | |||
| maxQueueSize | 1000 | The maximum number of items to queue before starting to drop old ones. | No |