Copilot Best Practices and Known Limitations
This document outlines the best practices for using Gainsight Copilot effectively and highlights current known limitations. It is intended for Gainsight administrators and experienced users who configure or actively use Copilot capabilities.
Overview
Gainsight Copilot empowers users to extract insights and automate analysis through intelligent queries. This document provides best practices to optimize Copilot usage and outlines current feature limitations to ensure effective and accurate use.
Best Practices for Creating Key Definitions
Key Definitions guide how Copilot understands and responds to user queries. To ensure accurate and consistent results, follow these best practices when creating or editing a Key Definition.
Data-Type Key Definition
Data-type Key Definitions allow admins to define how Copilot uses structured data from Gainsight objects to answer queries. For Data-type Key Definitions, you define logic by selecting a report, adding instructions, or using both, as follows.
- Use a report when you want Copilot to import data from an existing report.
- Use instructions when you want to define the logic from scratch.
- Use both report and instructions when you want to add some constraints on top of the imported report data. Copilot applies the report followed by processing admin instructions.
Create Effective Key Definitions
Key Definitions help Copilot interpret user queries and deliver accurate responses. Follow these guidelines to create high-quality Key Definitions:
Use Clear and Descriptive Names
- Avoid using acronyms.
- Choose names that reflect business intent clearly. Example: “Renewals in Next 90 Days".
Write Specific Intent-Driven Descriptions
- Describe the scope, logic, and purpose.
- Avoid vague or overly generic descriptions.
Example
- Name: At-Risk Renewals (Next 90 Days)
- Description: Includes companies with renewal dates in the next 90 days, flagged as "at risk" based on health scores.
Add Instructions One at a Time
Instructions are optional and can be used independently or alongside a report in Data-type Key Definitions.
Avoid combining multiple logic statements in a single instruction. This improves clarity and helps Copilot interpret them accurately.
Clearly State the Fields and Objects Referenced in Instructions
Always mention the exact fields and objects involved so Copilot can interpret the instruction accurately. For example: Specify: ARR field in the Company object or Status in the CTA object. This prevents misinterpretation by Copilot, especially in Instruction Key Definitions.
Test Each Key Definition Individually
After saving a Key Definition, run a test query to verify that it returns the expected results before creating or updating another one.
Validate Using the Output Section (for Data type Key Definitions only)
The Output section displays the final logic generated from a report, instructions, or both, allowing you to review the results. Use the output section to verify results when working with Data-type Key Definitions.
- Review the Output tab and sources to confirm the definition is returning correct results.
- Adjust filters and logic as needed.
_Review_the_Output_tab_to_confirm_the_definition_is_returning_correct_results._.jpg?revision=1)
Copilot displays a maximum of 5000 records in the output preview.
Leverage Existing Definitions
Reuse existing definitions to save time and ensure consistent results.
-
Only supported objects (Company, Call to Action, Task, Success Plans, Activity Timeline, and User) can be used in Key Definitions. Using unsupported objects results in an error, as shown in the Summary section of the image.

- Copilot refers to related Key Definitions while processing queries.
- Ensure consistency across all Key Definitions created using the same object.
Copilot evaluates multiple related Key Definitions and selects the most relevant ones based on the query context.
Format Queries for Better Results
Use Structured Format: Prefer structured conditions with supported filters.
Correct Format Example
List CTAs where:
- Type is Product Investment Request
- Status is one of: Submitted to Product, New, WIP, Stalled
- Owner is ABC XYZ
Follow Naming Conventions for Entities
- Use single quotes around entity names.
- Specify the entity type clearly.
Example: Summarize 'Enterprise Support Risk' CTA. Include associated tasks and summaries.
Use Clear and Actionable Prompts
For example: Summarize all available information on the 'Q4 Renewal Risk' CTA including all open tasks.
If the response is incorrect, try rephrasing your query in a new chat.
Timeline Query
Ask questions about Timeline entries to get insights from customer interactions.
Best Practices
- For open-ended questions related to Timeline, Copilot applies filters (if specified) before retrieving results:
- If the query includes a specific filter such as date range, segment, Copilot first applies the filter and then retrieves the 50 most recent Timeline entries from the filtered results.
- If the query does not include any filters, Copilot analyzes all available Timeline posts relevant to the user’s question.
Example query: Which customer in the enterprise segment expressed negative sentiments in the last month?
IMPORTANT: Avoid broad, cross-account queries. Due to the 50-entry limit, such queries may return incomplete results.
Supported Query Types:
- Structured (tabular data)
- Unstructured (open-ended question, non-tabular format)
Not Fully Supported:
- Views created by users in CTA or Success Plans
- Playbooks and Gantt charts
Do’s and Don’ts for Key Definitions
| Do | Don’t |
|---|---|
| Use clear business terminology | Use internal acronyms that are not easily recognizable to users |
| Be descriptive and specific | Leave descriptions vague and generic |
| Include intent in the description | Provide clear, business-relevant descriptions with intent and logic (required field) |
| Match how users naturally ask questions | Use overly technical terms unless commonly used |
Examples of Good Practice
| Field | Good Example | Why It Works |
|---|---|---|
| Name | Backlog CTAs | Clearly communicates that the definition is focused on overdue CTAs. |
| Description | Backlog CTAs are all open Call to Actions that have passed their due date and are not yet closed. They help users track overdue work and ensure timely follow-ups. | Provides clear criteria of open and past due and explains the business value by tracking overdue actions for better follow-through. |
Structured versus Unstructured Query Support
Copilot supports different types of Timeline queries depending on how the question is structured and the scope of analysis.
| Query Type | Description | Example | Support |
|---|---|---|---|
| Structured | Copilot returns tabular data with specific fields | How many activities were there for company A? | Supported |
| Unstructured (Account-Level) | Analyzes note content and standard/custom fields for one account | From my last EBR activity for ‘Acme Corp’, summarize goals. | Supported |
| Unstructured (Cross-Account) | Queries across multiple accounts or activities | Summarize business goals across all EBR activities. | Supported |
Known Limitations
Copilot currently has the following restrictions:
| Area | Limitation |
|---|---|
| Query Volume | Max 5000 records returned in Output |
| CTA and Success Plan Views | User-created views are not queryable |
| Success Plan | Cannot analyze Gantt Charts |
| Playbooks | Cannot analyze Playbook content |
Tips to Optimize your Copilot Experience
Use these tips to get faster, more accurate answers from Copilot.
- Preview data before applying Key Definitions to ensure alignment with business expectations.
- Be clear and specific when writing queries.
- Use action-oriented prompts such as Summarize, List, or Explain.
- Avoid using vague or generic language.
- Use terminology that matches how users naturally ask questions.
Copilot Best Practices
To harness the full potential of Copilot and ensure a seamless, productive experience, it’s crucial to follow certain best practices. This section provides a comprehensive understanding of how to effectively interact with Copilot. By offering clear context, leveraging sample queries, using follow-up prompts effectively, and managing sessions efficiently, users can enhance the accuracy and relevance of the AI's responses. These practices not only improve user experience but also maximize the AI’s capabilities, leading to more insightful and actionable outcomes.
- Provide Clear Context: Always specify the full name of Company or User while writing the query. The Copilot's Natural Language Processing (NLP) engine parses user input to determine the context. Clear context helps the engine to direct the query appropriately.
- Example
- Global Query: Show me the overall customer feedback for the last quarter.
- Specific Company Query: What was the customer sentiment for Company ‘X’ in the last month
- Example
- Use the Hash (#) Selector for Accurate Company Matching: To improve accuracy when referencing companies, especially those with similar names, use the # symbol to trigger the company selector in the query input. This helps eliminate ambiguity and ensures Copilot returns results based on the exact company record. To use the hash selector:
- Type
#to insert#""with the cursor placed inside the quotes. - Begin typing the company name inside the quotes. A list of matching company names appears as you type.
- Select the correct company from the list to include an exact reference in your query.
Example: Show me all the CTAs for #”Acme”
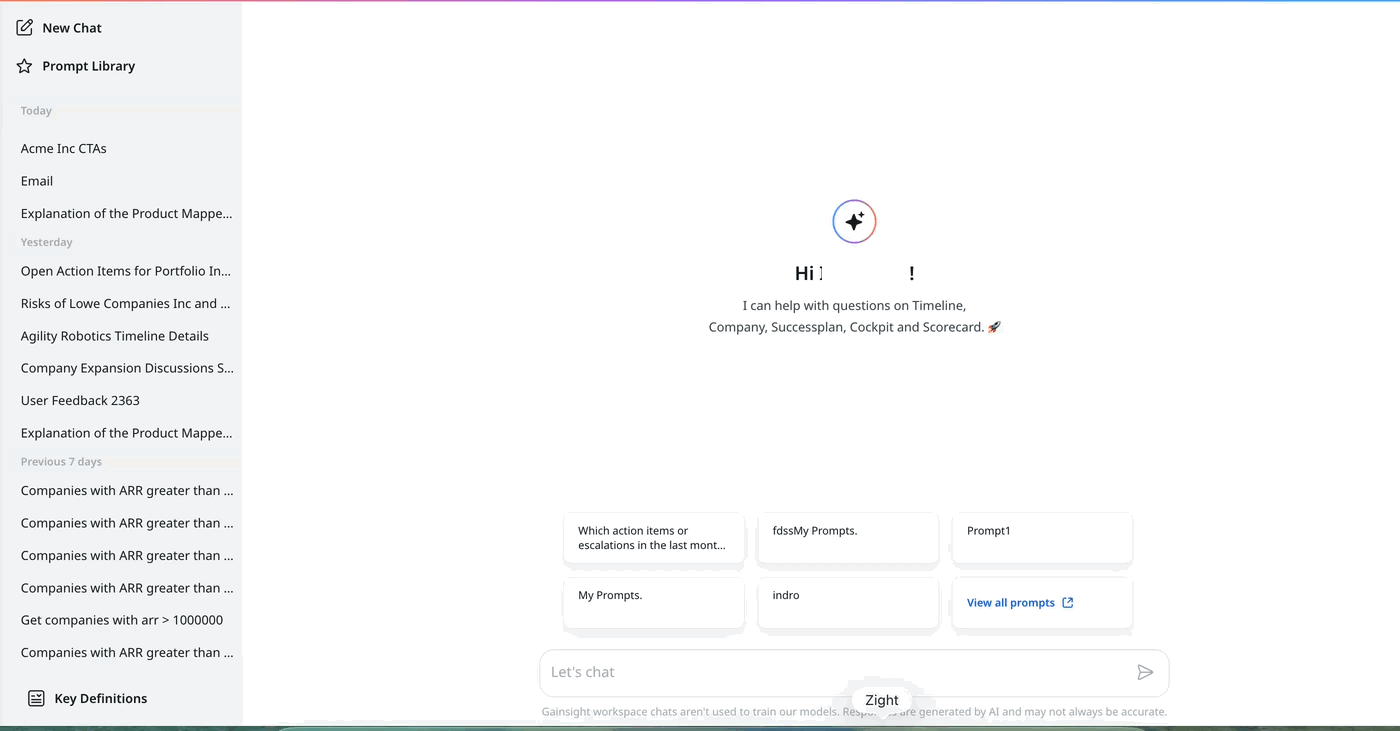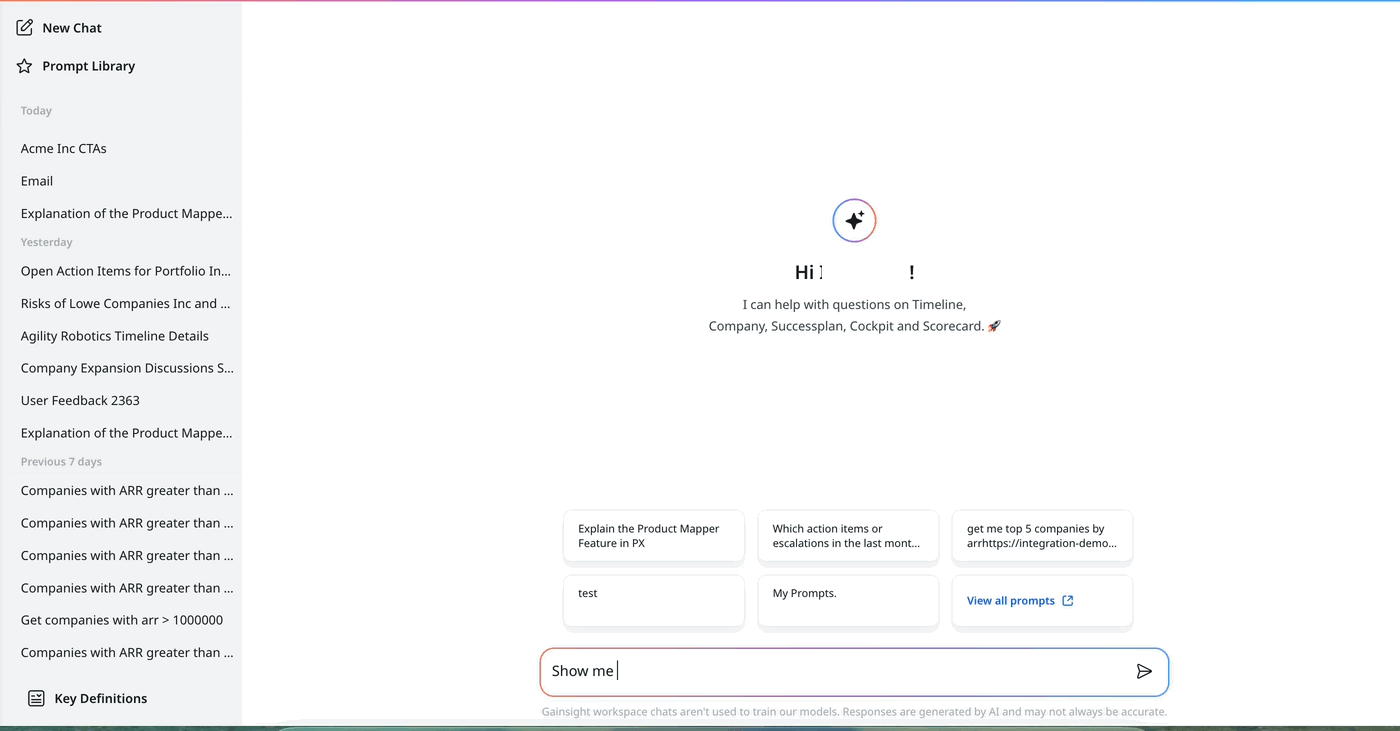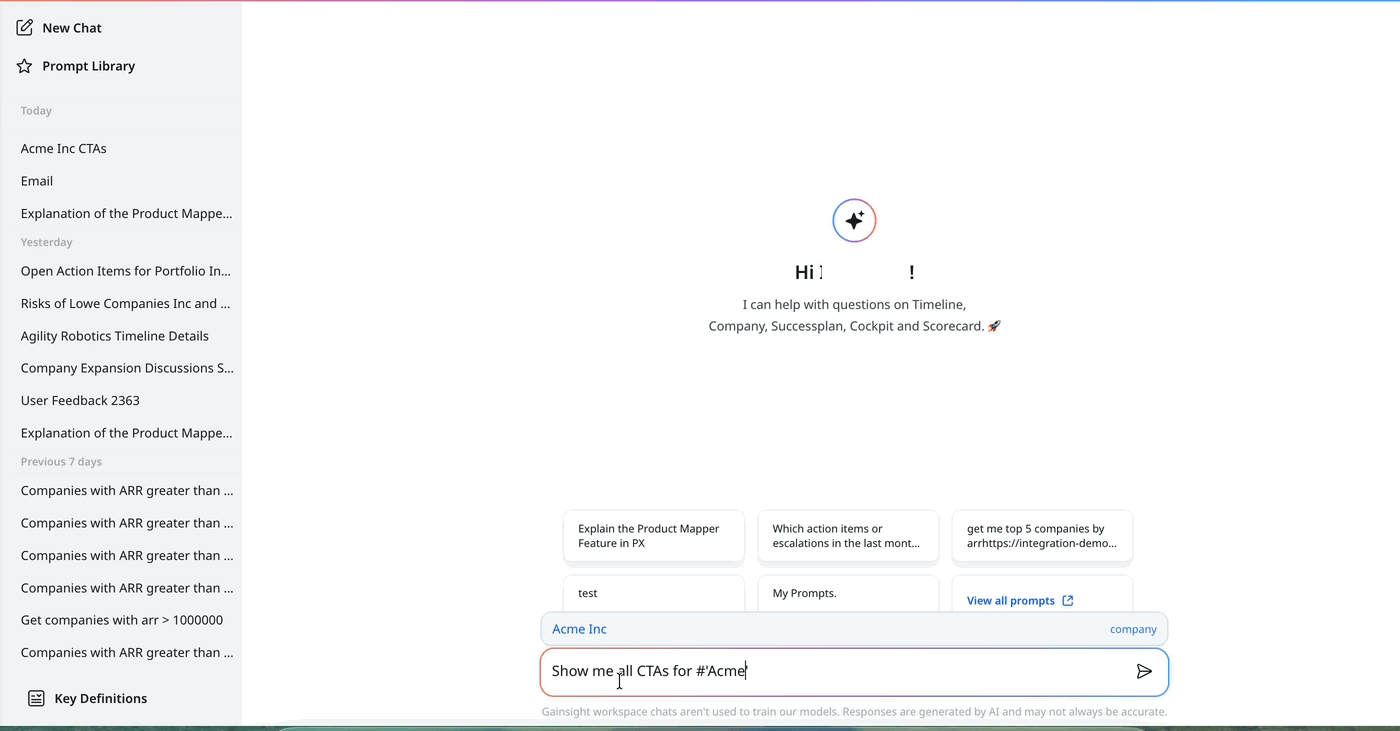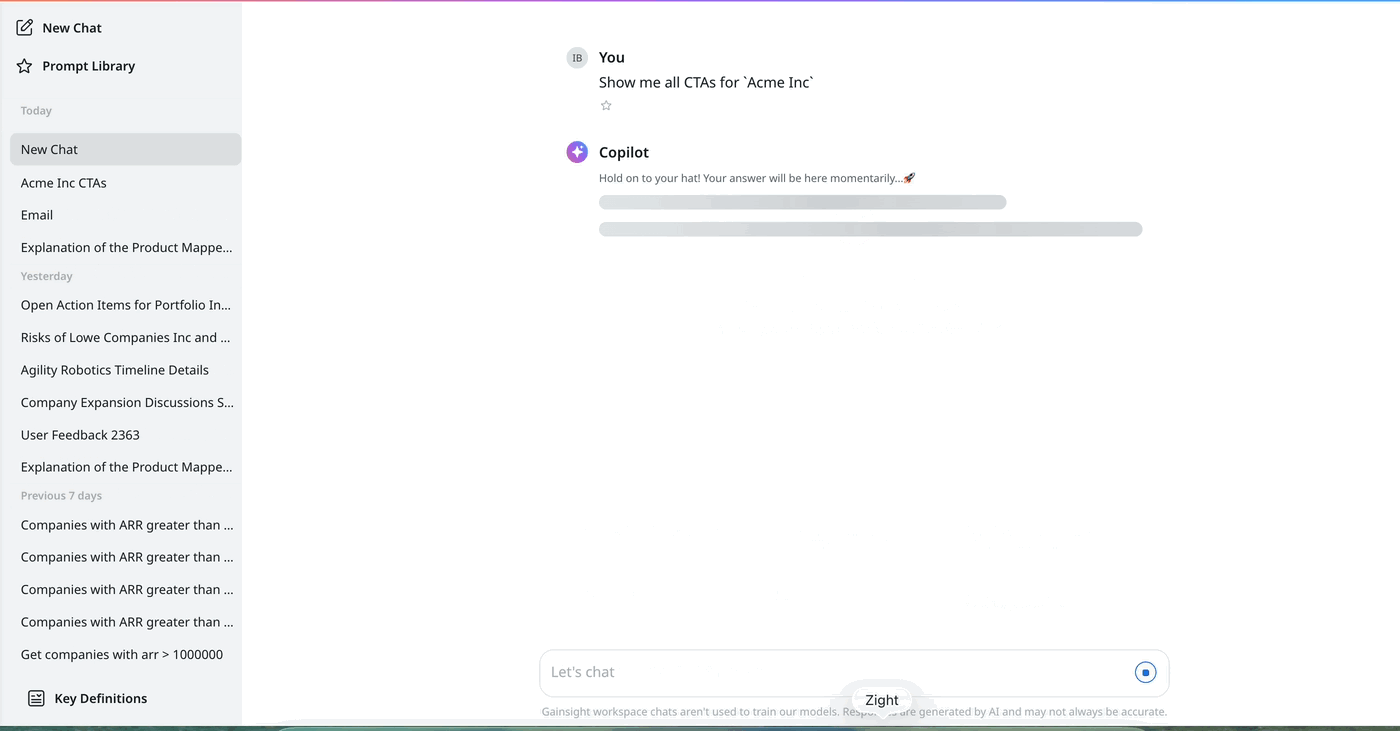
- Follow-Up Effectively: For optimal performance, queries should ideally involve only one service. While multiple services can be utilized, breaking down the query into sequential, single-service queries is recommended In case a query requires multiple services asked in steps one at a time as follow up questions . Follow-up questions help to dig deeper into the initial query results, providing more detailed insights.
- Example
- Initial Query: What were the main issues raised by Company ‘X’ in the last quarter
- Follow-Up Prompt: Can you provide more details on the issue related to product delivery?
- Example
- Queries such as "summarize my last three meetings" apply a user filter.
- Tip: When asking a question about a specific entity such as a Company, Relationship, Success Plan, CTA, or Task follow these for best results:
- Use single quotes around the entity’s exact name
- Clearly mention the entity type
Example: Summarize 'New CS Project - Assign Sheet' CTA. Don’t miss out on any information.
